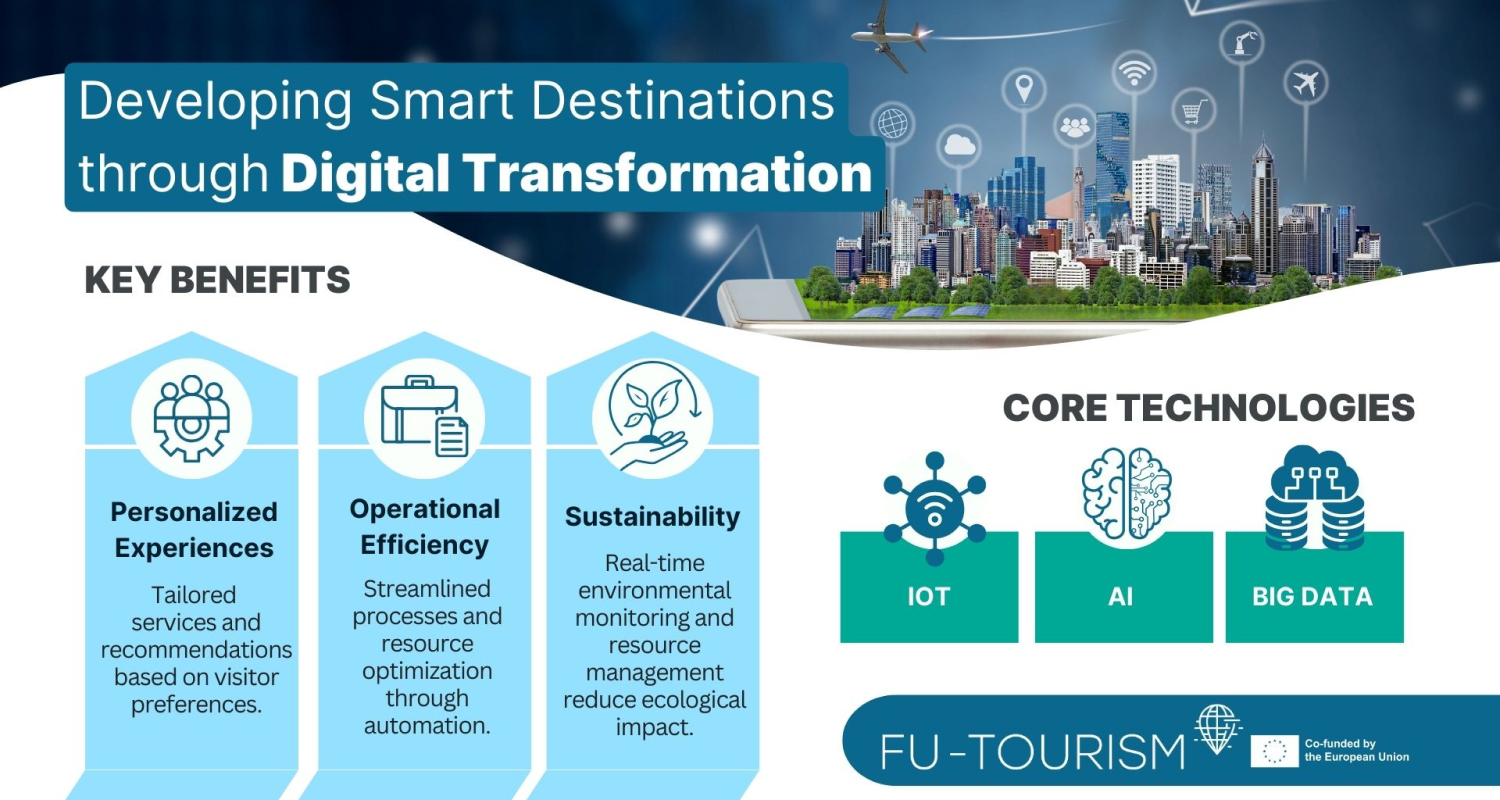
Harnessing Sustainability and Digitalization in Tourism
The tourism industry on the European landscape couldn’t be more diverse, covering all possible tourist areas, from sunny summer destinations to snowy winter resorts. Some countries are at the forefront of integrating sustainability and digitalisation to create a more responsible and innovative sector. This change is embodied in several key initiatives in the regions, represented by a wide range of initiatives from eco-friendly ski resorts to data-driven tourism practices.
Sustainable Winter and Engaging Summer Tourism
Ski resorts are leading the way in sustainability. If we look at the ski resorts in Austria, for example, there are several SMEs that have already implemented environmentally and socially sustainable solutions for their areas. These initiatives include the development of solar-powered chairlifts that generate 60,000 kWh per year and the promotion of electric vehicles with 22 charging points on site. In terms of social sustainability, the introduction of a four-day working week aims to improve work-life balance while contributing to an ambitious target to reduce CO2 emissions by 77% by 2030 compared to 2016/17.
Similarly, other resorts have made significant progress, reducing electricity related CO2 emissions by 9,800 tonnes and fuel emissions by 42% for the 2023/24 season. A key strategy is to switch to hydrogen-powered vehicles, which are expected to reduce emissions by 95%. These initiatives are supported by public-private partnerships with the German and Austrian railways, ensuring that visitor transport is also in line with environmental objectives.
Summer tourism is also evolving, with innovative projects aimed at educating and engaging visitors on environmental issues. There are initiatives that focus on making the effects of climate change more visible and tangible, highlighting rising average temperatures and their impact on the local environment. This approach highlights the need for increased visitor awareness and action. In the cultural sector, efforts are being made to achieve carbon neutrality at major events. Certain music festivals that initially produced a significant amount of CO2 emissions successfully achieved carbon neutrality within a year. This emphasis on transparency and environmental responsibility sets a new standard for similar events within several regions.
Digitalization and Innovation
The tourism sector has also proved to be an ideal place to test innovative and digital ideas. For example, the concept of a Tourism Data Space is being piloted in Tyrol, Austria, using live data, mobile telecommunications and advanced prediction engines to optimise tourism services. This initiative aims to create new business models, improve resource planning and provide actionable insights for local tourism boards. This is also in line with the overall strategy of FU-TOURISM, as the pilot activities will be carried out in two important regions, internationally known as green UNESCO destinations, namely the city of Porec-Parenzo and the city of Valencia.
The adoption of digital tools and data-driven strategies is also crucial to address the labour shortage highlighted in several studies, such as one published by McKinsey in 2023. By leveraging digital capabilities, the tourism sector will be better equipped to enhance the customer experience while addressing labour challenges. During the course of the project, FU-TOURISM will therefore not only focus on digital, economic and ecological perspectives, but also on inclusive and social aspects, which will find their way into the implementation of the project’s tasks.
Tourism’s integration of sustainability and digitalization is setting a global standard for the future of the industry, paving the way for a sector that can thrive in harmony with the planet. This evolving approach demonstrates the potential for tourism to lead the way in creating a more sustainable and forward-looking global landscape.